Definition of compound annual growth rate:
Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is a measure of growth rate of an investment over a specified period of time.
Formula:
The following formula can be used in the calculation of CAGR:
 Stock split is a technique used to infuse liquidity and make share’s prices more affordable for investors. A company, whose share’s prices are beyond the reach of average investors, splits its shares by increasing the total number of outstanding shares. Usually, the shares are increased in the multiples like 2 or 3 for 1, which means that the shareholder will have two or three shares for every share held by him earlier.
Stock split is a technique used to infuse liquidity and make share’s prices more affordable for investors. A company, whose share’s prices are beyond the reach of average investors, splits its shares by increasing the total number of outstanding shares. Usually, the shares are increased in the multiples like 2 or 3 for 1, which means that the shareholder will have two or three shares for every share held by him earlier.
It should be kept in mind that, only the number of shares is increased and not the total market capitalization of the company. So, stock split results in the decrease in share’s price and thus they become more affordable for investors.
XYZ Ltd has total 100,000 outstanding shares, each valued at INR 5,000. So the total market capitalization of the company is 500,000,000. Let’s suppose that the company splits its shares into 2 for 1.
Now,
The total no. of shares is = 100,000 × 2 = 200,000
But the total market capitalization of the company is = 500,000,000.
So, the share price will be = 500,000,000/200,000 = 2500.
An index divisor is a mathematical number, used in the calculation of a stock index like Sensex & Nifty. This number is calculated by dividing the base year’s index value by base period’s market capitalization of the concerned stock market.
Every stock market’s index (like Nifty) is calculated by making a comparison between current market capitalization of the constituents of an index and base year’s market capitalization of the constituents of that index. This divisor is the only link between original base period value and the current stock market index’s value.
As the base year for a stock market remains unchanged, the value of index divisor also remains the same.
For the calculation of Sensex, base year is 1978 – 1979 and base index (value of Sensex at that point of time) is 100. Let’s suppose at that point of time, market capitalization of the constituents of Sensex was 60,000 then, the
![]()
Free float market capitalization is a term used in stock market. The term refers to that proportion of total shares which are actually available for trading in stock market. It means that out of total issued shares, if promoters’ holdings, government holdings and other locked in shares are excluded then remaining shares represent free float market capitalization.
So if put it simply free float market capitalization is the proportion of total shares available for trading to the general public.
Let’s suppose that company XYZ Limited has issued 1, 00,000 shares of INR 10 each. Out of which 10,000 shares are held by promoters and 5,000 shares are held by the government.
Now,
Total market capitalization of the company is = INR 10, 00,000 (1, 00,000 × 10)
Total locked in market capitalization is = INR 1, 50,000 (15,000 × 10)
Working capital refers to the amount of capital used by a company to perform its daily operations. It is simply the difference between current assets and current liabilities of a company.
It can be used to measure:
a) the short term financial health and
b) efficiency of a company to meet its short term liabilities.
The amount of negative or very less working capital indicates that the company is not able to pay its current liabilities within given time period. On the contrary, it indicates that the company has either generated a large number of credit sale or it has invested a big amount of capital in its current assets, that also is not good for company.
The given formula can be used for this purpose:
![]()
Suppose, XYZ Ltd has following figures in its balance sheet:
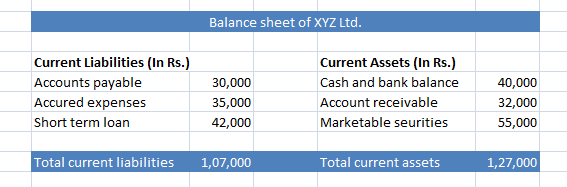
Total current assets of the company = 1,27,000
Total current liabilities of the company = 1,07,000
By using the given figures and formula, working capital for XYZ Ltd is:
= 1,27,000 – 1,07,000 = 20,000.