Before reading about the different types of asset, it is advisable to know the meaning of asset.
Meaning of asset:
In context of a company, an asset is a resource having some economic value which can be measured. Assets are used to increase the cash-flows for a firm. Therefore, these are bought for the purpose of adding value to a firm.
Different types of asset:
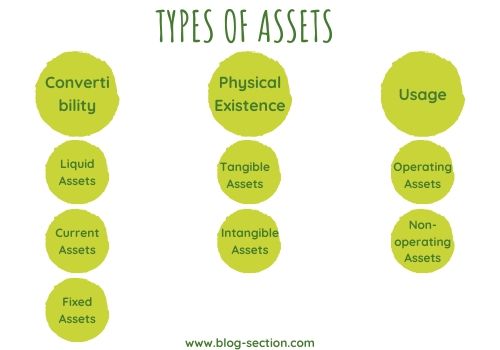
There are 7 major types of asset which falls under 3 main categories:
Convertibility: Liquid, Current and fixed assets
Physical Existence: Tangible and intangible assets
Usage: Operating and non-operating assets
On the basis of convertibility:
There are 3 main types of asset under this category:
Meaning of current assets:
Current asset refer to those assets which can be converted into cash within a short period of time. These assets are used to pay off short term debt obligations of a company. In other words, the main purpose of having current assets is to pay off current liabilities.
Example of current assets:
Below is a complete list of these assets:
- Cash and bank balance,
- Accrued interest,
- Stores and spare parts,
- Loose tools,
- Stock in trade,
- WIP,
- Accounts receivable etc.
Treatment of current assets:
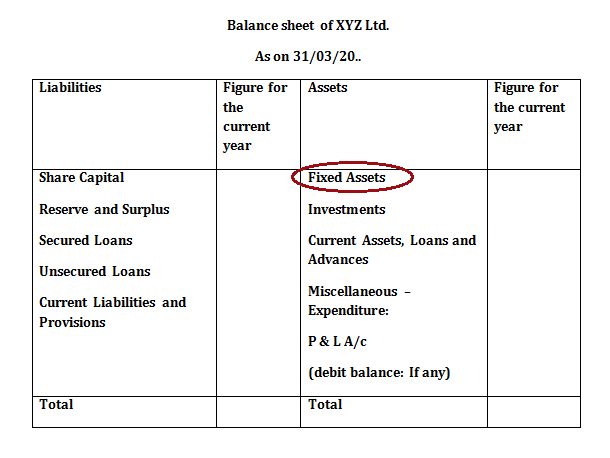
These assets are shown on the assets side on a balance sheet as highlighted in below image:
Total amount of these assets, given on the balance sheet, is also used to calculate working capital for a company. Working capital is used to pay off day to day expenses of a company.
Read about: Difference between liquid assets and current assets
Meaning of fixed assets:
Fixed assets are used to generate income for a business enterprise over a longer period of time. These assets are not purchased for the purpose of selling them to business customers or its end users. This characteristic differentiates fixed assets from current assets.
It should be noted that in some countries like India, these assets also include intangible assets like goodwill of the firm, patents, trademark etc.
Example of fixed assets:
A common list of these assets includes:
- Land & buildings,
- Leasehold premises,
- Railway sidings,
- Plant & machinery,
- Furniture,
- Patents and trademarks,
- Live stock,
- Vehicles etc.
Treatment of fixed assets:
Fixed assets are an important part of a company’s balance sheet and are shown on the asset side. The figures given on the balance sheet are net values of these assets.
Net value means values which remained after deducting depreciation.
Meaning of liquid assets:
These assets are considered more liquid than current assets in sense that they can be converted into cash within a very short time (90 days).
Example of liquid assets:
- Cash,
- Bank balance,
- Accounts receivable etc.
Liquid assets are assumed to be converted into cash at any point of time. That’s the reason why inventory (as it is difficult to convert, when needed) and prepaid expenses (cannot be converted into cash at all) are not considered as liquid assets.
On the basis of physical existence:
There are 2 main types of asset under this category:
Meaning of tangible assets:
As the name suggests, these are the assets which can be seen and touched.
Example of tangible assets:
- Property,
- Plant,
- Equipment,
- Furniture,
- Machinery etc.
Meaning of intangible assets:
Unlike tangible assets, intangible assets can be seen or touched but have business value.
Example of intangible assets:
- Patents,
- Copyright,
- Goodwill,
- Trade secrets,
- Permits,
- Corporate intellectual property etc.
On the basis of usage:
There are 2 main types of asset under this category:
Meaning of operating assets:
These are the assets which are used to perform day to day activities in an organization.
Example of operating assets:
- Cash
- Stock
- Building
- Machinery
- Equipment
- Patents
- Copyrights
- Goodwill etc.
Meaning of non-operating assets:
These assets are not used in day to day operation but they still generate revenue.
Example of non-operating assets:
- Short-term investments,
- Marketable securities,
- Vacant land,
- Interest income from a fixed deposit etc.



